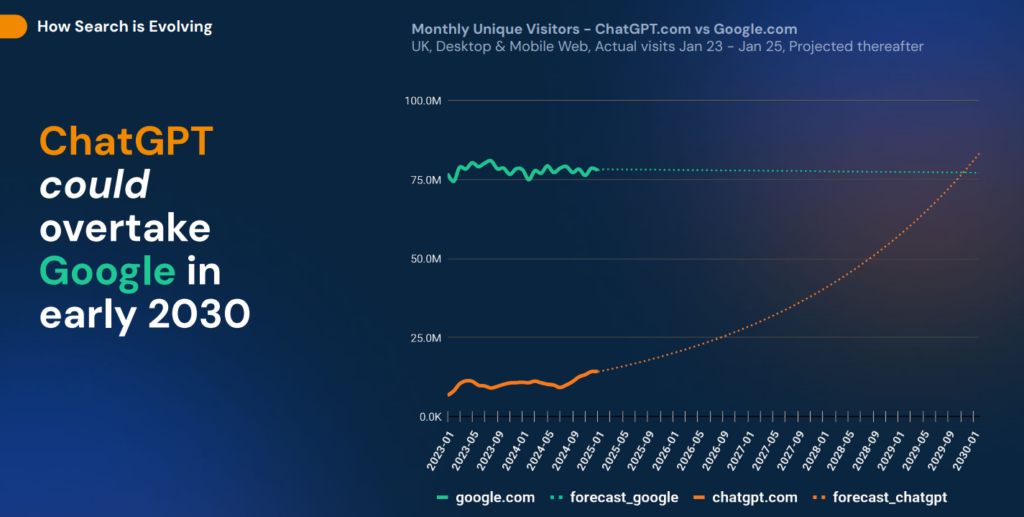
Search is undergoing a fundamental change. Based on multiple qualitative studies and authoritative sources, we can clearly see the direction Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is heading. Recent projections — presented by Baruch Toledano from Similarweb during his talk at BrightonSEO — indicate that ChatGPT could overtake Google as the dominant search interface as early as 2030. These findings highlight the importance for businesses to adapt quickly to remain visible and competitive in this evolving digital environment.
Shifting user behavior and demographics
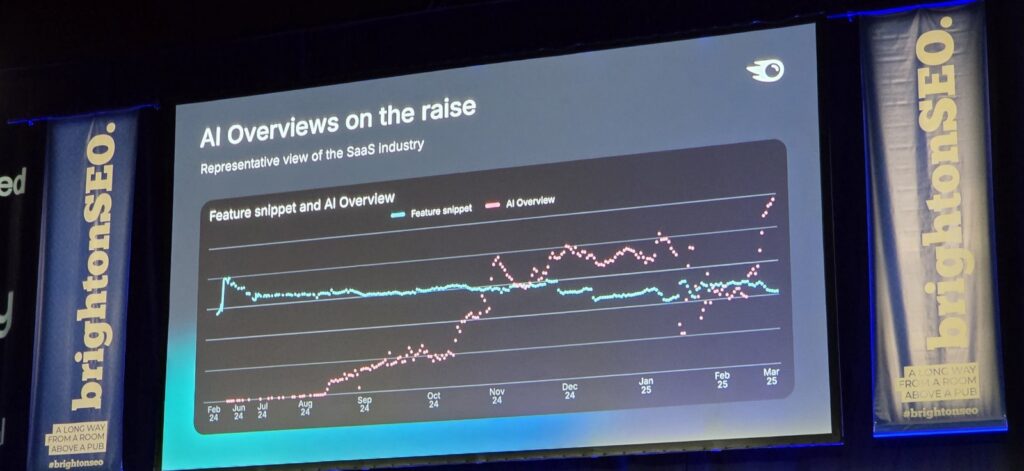
Recent studies illustrate significant changes in user search behavior. According to Semrush research focused on the SaaS industry — as presented by Marcus Tober during his keynote at BrightonSEO — AI-generated overviews are quickly replacing traditional featured snippets.
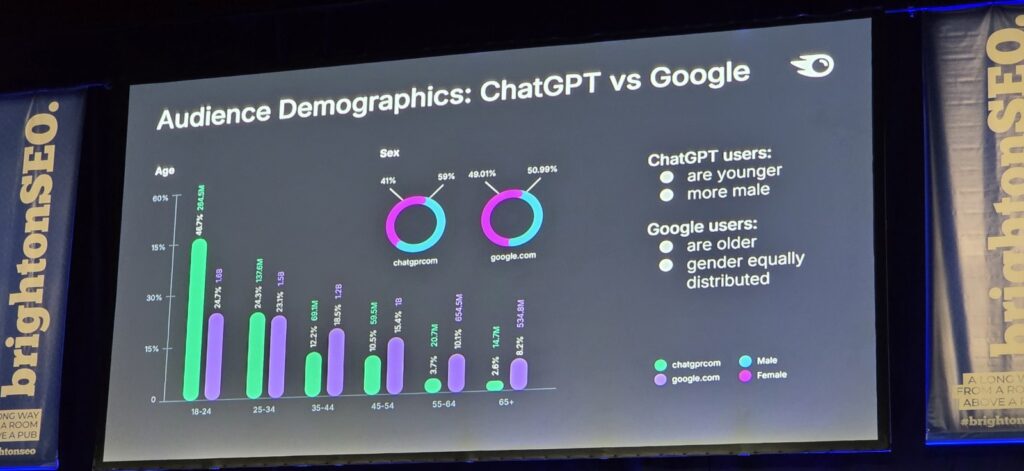
Younger demographics, especially students, are adopting generative search tools significantly faster than older users (aged 35-65+).
Supporting this shift, SimilarWeb research reveals notable differences in query lengths. Google’s average search query length stands at 3.2 words, whereas ChatGPT prompts average 37.1 words. Users are clearly moving towards seeking more detailed, context-rich responses from generative AI platforms.
Content should mirror conversational user behavior by emphasizing natural language structure, addressing user intent holistically, and incorporating question-based content. To put this into practice, integrate FAQ-style content blocks, use long-tail queries in headings and subheadings, and create articles that are driven by real-world use cases.
Pieter Verschueren, Co-founder of Rankshift and Depends SEO agency
User engagement and traffic quality
Generative AI-driven traffic not only differs in behavior but also quality. Users arriving from platforms like ChatGPT demonstrate significantly higher engagement levels, reflecting their deeper informational intent and refined search queries.
On average, they spend around 11 minutes per session compared to Google’s average of 8 minutes, suggesting a more thorough exploration of website content. Additionally, these users visit notably more pages per session (13.3 pages vs. 11.4 pages on Google), which highlights the comprehensive nature of interactions driven by generative AI platforms.
This deeper engagement underscores the potential value of optimizing content specifically for generative AI search experiences, aligning closely with user expectations for detailed, contextually-rich information.
The evolution from backlinks to citations
Traditional SEO strategies, such as backlink building, are evolving. Context-driven content and citations are becoming essential for visibility in AI-driven search results.
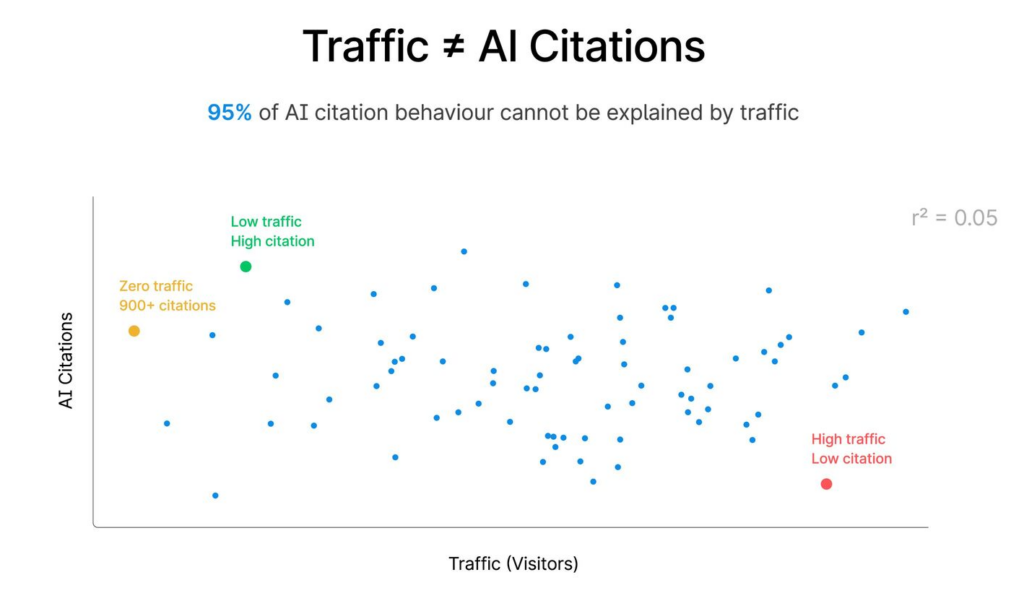
Before we dive deeper into this matter, it is important to know that traffic is not the same as AI citations. 95% of AI citation behaviour cannot be explained by traffic.
Well-known SEO specialist Eli Schwartz puts it:
“In this paradigm, links don’t need to be hyperlinked (LLMs read content) or restricted to traditional websites. Mentions in credible publications or discussions sparked on professional networks (hello, knowledge bases and forums) all enhance visibility within this framework.”
Eli Schwartz, Author of Product-Led SEO, Strategic SEO & Growth Advisor
Referral traffic from ChatGPT is growing fast. According to SimilarWeb, clicks from ChatGPT to other websites have increased by a huge 1,282% compared to last year. Some sites, like Rome2Rio, have seen big jumps in visitors because of this. This shows something important: ChatGPT and other language models do send users to websites—it’s not a “zero-click” situation. That means getting traffic from these models is now a real strategy.
To take advantage of this, figure out which types of content LLMs are linking to, and keep track of the exact pages (URLs) getting that traffic. Then, use the same layout and style in other related content to grow your results. The most cited domains in LLMs are Wikipedia and UGC sites like Reddit, YouTube, LinkedIn, Quora and Yelp.
Another interesting insight states that 97,2% of AI citations cannot be explained by backlinks. Sites with fewer backlinks often receive significantly more AI citations.
An Ahrefs study reveals important insights:
- 63% of websites receive traffic from AI-driven searches.
- ChatGPT (79.5%), Perplexity (15.6%), and Gemini (4.8%) dominate AI-generated traffic.
- AI-generated overviews have decreased traditional clicks by 30%.
- AI queries are predominantly informational (99.2%), navigational (20.3%), commercial (5.8%), and transactional (4.0%).
Additionally, AI-generated content not only reduces costs significantly (average $131 per piece vs. $611 for human-written content) but also boosts organic traffic growth (4.87%).
Technical SEO considerations for GEO
Bing indexing is mandatory for visibility in ChatGPT. If your website isn’t indexed by Bing, it will be invisible to ChatGPT’s web-enabled models. Make sure your site is indexed to ensure it can be found.
Businesses must also consider how AI crawlers index content. AI bots such as OAI-Searchbot, GPT-Bot, ChatGPT-User, PerplexityBot, and ClaudeBot currently face difficulties rendering JavaScript-based content. Ensuring visibility requires server-side rendering and structured HTML content.
As part of technical optimization for Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), implementing an llms.txt file can significantly improve your site’s visibility to AI-driven search engines. Similar to robots.txt in traditional SEO, llms.txt acts as a signal to large language models (LLMs), guiding AI crawlers on which content to access, prioritize, or exclude. It helps ensure your content is AI-readable, aligns with natural language generation requirements, and increases the likelihood of inclusion in AI-generated responses. This lightweight file supports faster and cleaner crawling.
AI optimization vs. traditional SEO
The key differences between traditional SEO and AI optimization strategies include:
- Traditional SEO emphasizes keywords, meta tags, and hierarchical structures.
- Generative AI prioritizes context, relevance, concise answers, and regularly updated content.
- Older content often ranks well in Google, whereas generative AI favors fresh and continually refreshed content.
Optimizing for generative AI involves:
- Regularly refreshing content with precise, clear answers.
- Adding conversational FAQ sections.
- Monitoring platforms like social media, Reddit, Quora, and forums to discover trending questions.
- Conducting frequent audits of structured data and analyzing AI-generated query responses.
Leveraging tools and data for optimization
It’s important for brands to determine if generative AI references their content. AI visibility tools such as Ranksift help analyze source references. Collecting extensive prompt-output data and analyzing these with AI can reveal actionable optimization insights.
The future favors early adopters. Businesses that proactively manage their visibility on generative platforms, ensuring AI engines have accurate and current information, will build a sustainable competitive advantage.
Explore our article on effective GEO strategies, and take a look at our practical GEO checklist for additional insights.

